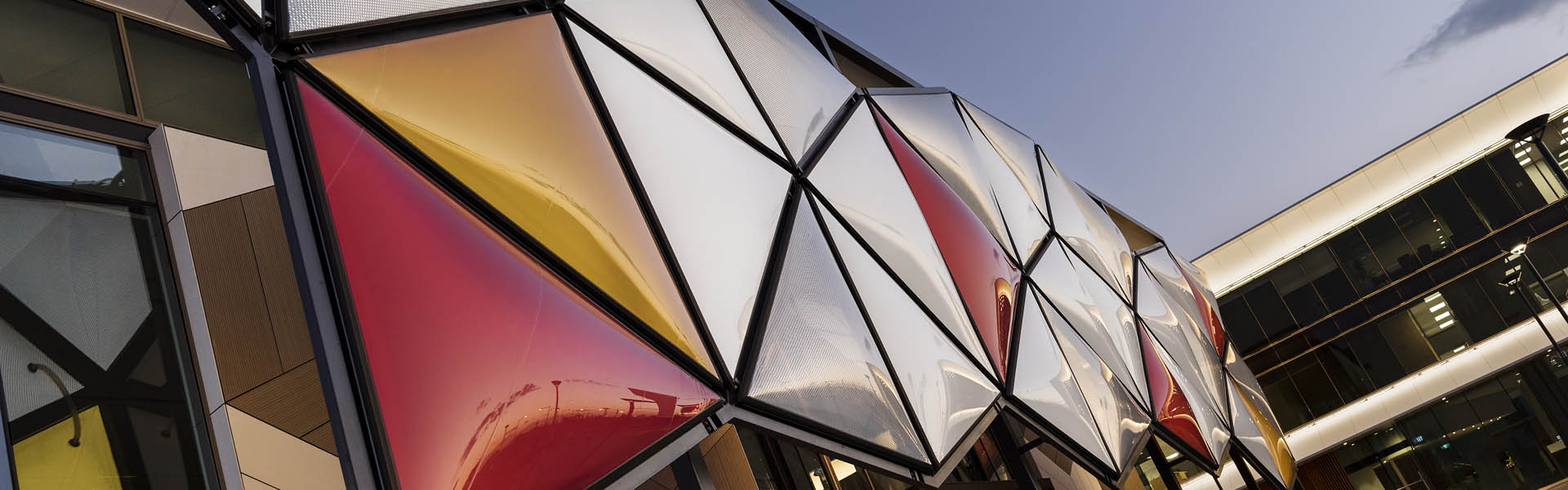
In the exciting world of architectural innovation, the choice of materials has a significant impact on the design possibilities that can be achieved. One material that has been making waves in the architectural field is ETFE. This remarkable transparent polymer is revolutionising the way roofs and facades can be designed. In this blog post, we will delve into the key components of an ETFE system, providing a comprehensive understanding of its important elements and exploring the wide range of possibilities offered by this extraordinary material.

Understanding ETFE: A Brief Overview
ETFE (ethylene tetrafluoroethylene), is a transparent polymer well known for its remarkable properties. It boasts high transparency, excellent durability, and resistance to environmental factors that makes it an ideal material for architectural applications.
Originally developed by DuPoint in the 1970s, ETFE’s initial use was in the aerospace industry. However, architects soon recognised its potential for creating lightweight, transparent structures that push the boundaries of traditional design.
ETFE stands out from conventional building materials such as glass due to its lightweight nature, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. These unique properties open up new possibilities for architects and designers seeking innovative solutions for their projects.
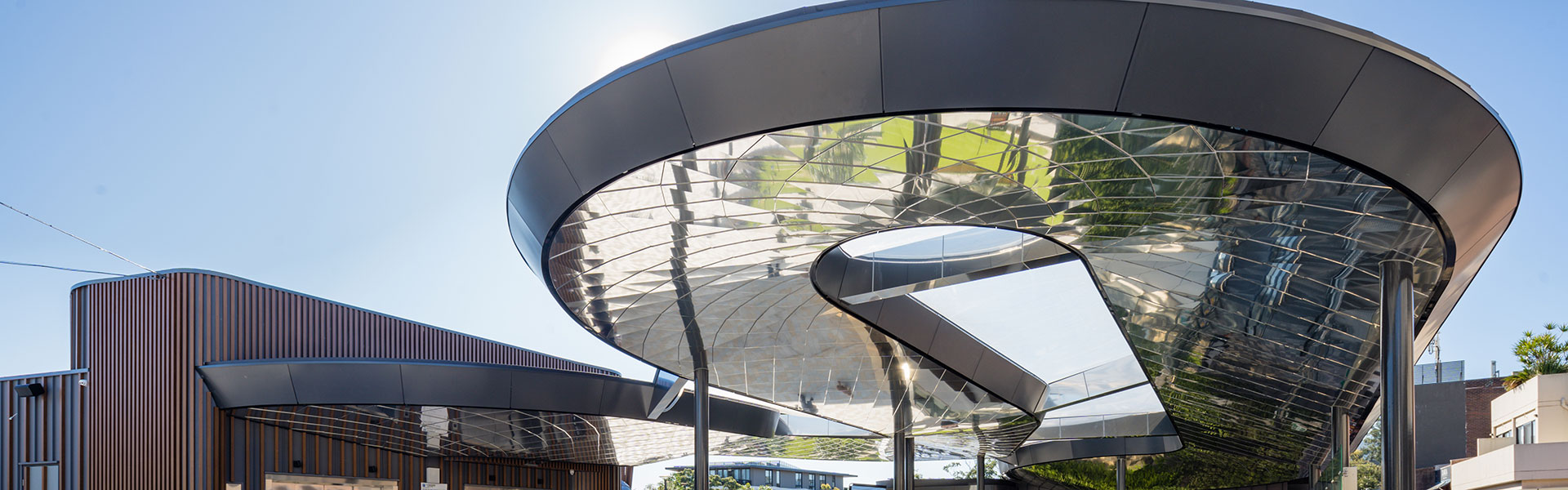

ETFE Film: The Core Material
At the epicentre of any ETFE system lies the ETFE film, a versatile component that serves as the foundational building block for creating transparent, lightweight and robust architectural elements. Typically manufactured in layers, the ETFE film possesses a range of exceptional properties, including high tensile strength, superb chemical resistance, and the ability to endure extreme weather conditions. ETFE film is available in single through to five-layer films – the most suitable configuration is based on the specific demands of the project.
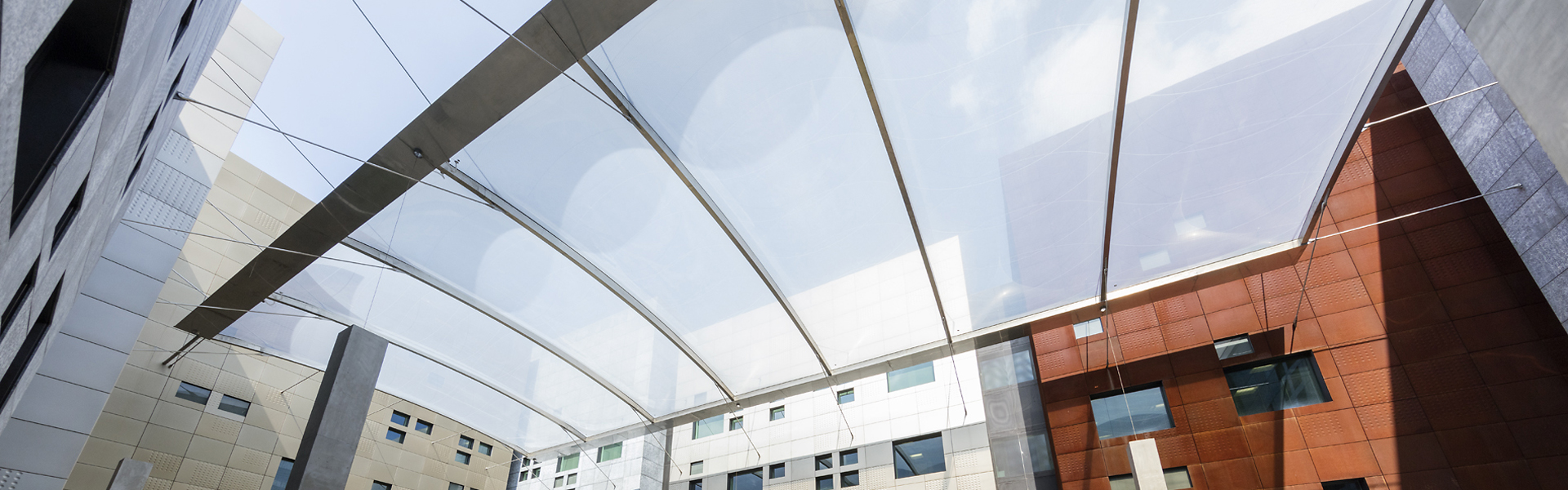

Structural Support
While ETFE exhibits inherent strength and resilience, ensuring the provision of adequate structural support is imperative for the longevity and stability of an ETFE system. The support structure demands detailed engineering to withstand varying environmental factors. Commonly, steel and aluminium serve as the go-to materials for crafting a support structure that is both lightweight and robust, seamlessly complementing the lightweight nature of the ETFE material.
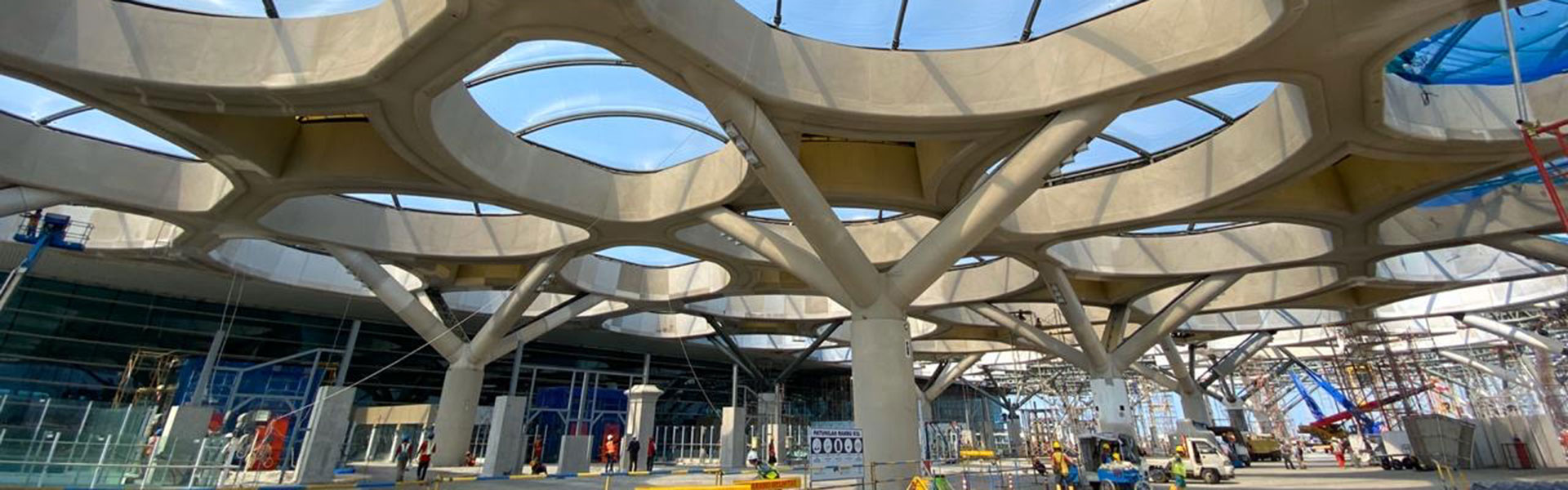

Installation Techniques
The installation of an ETFE system requires a meticulous approach to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The lightweight nature of ETFE facilitates easier transportation, handling, and installation. The process involves the careful tensioning of the ETFE film within the support structure to create a taut and secure membrane. Proper tensioning is paramount to prevent sagging and maintain the structural integrity of the system.
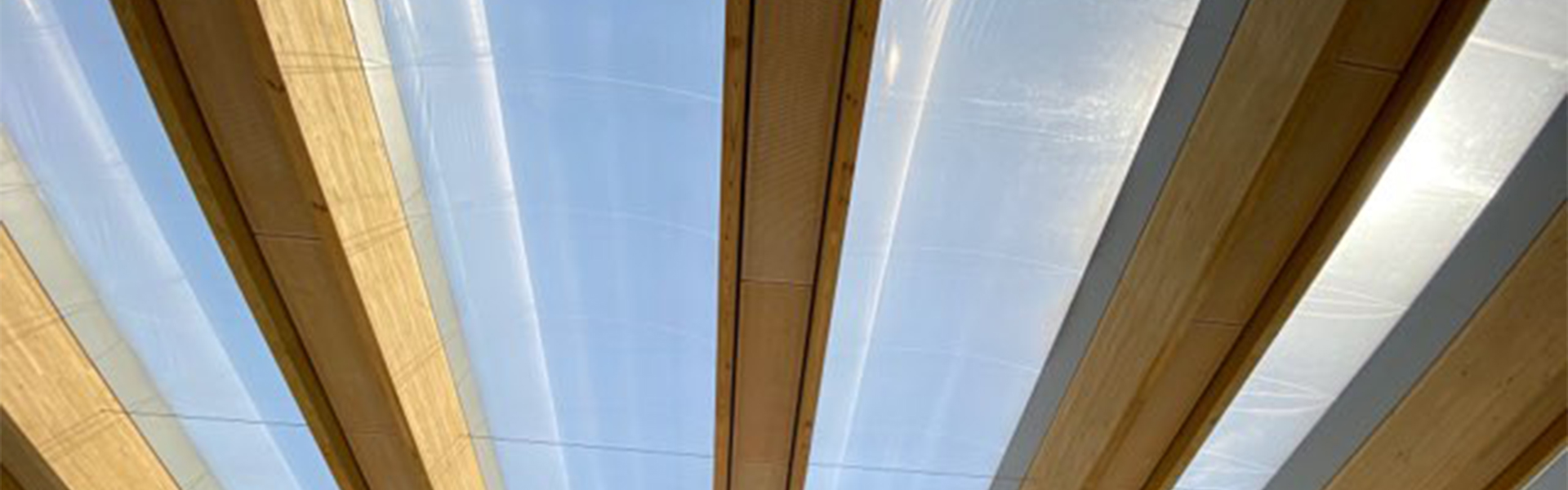

Thermal Control
Effective thermal control stands as a critical aspect of designing with ETFE, especially in regions characterised by extreme weather conditions. While ETFE possesses insulating properties, additional measures can be implemented to enhance thermal performance. One such measure involves incorporating a cushion of air between the layers of the ETFE film, significantly improving insulation. This air cushion acts as a barrier, reducing heat transfer and minimising temperature fluctuations within the enclosed space.
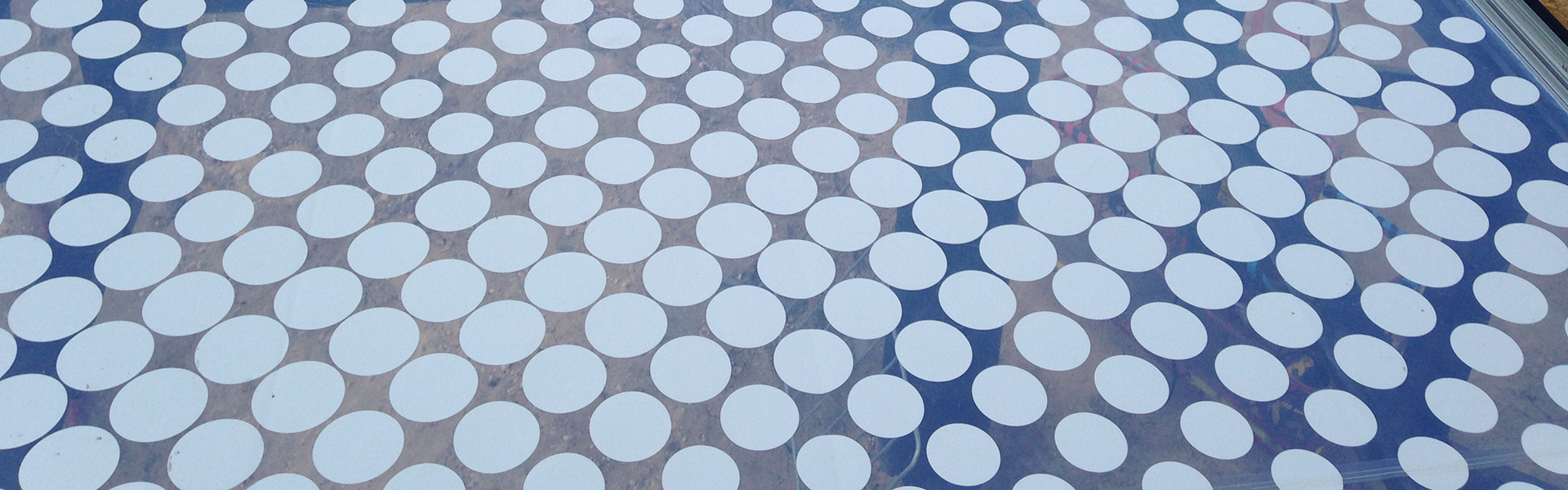

Customisation and Aesthetics
One of the key advantages of using an ETFE system for architectural applications is the wide range of customisation options available. These customisation options lie in the various frit patterns that can be applied to the surface of the material.
A frit pattern refers to the pattern that is printed in silver ink onto the surface of the ETFE film. This pattern not only enhances the visual appeal of the ETFE system but also assists in reflecting light both light and heat, before it filters through to the space below. Some common types of frit patterns include dot patterns, organic patterns, and custom designs.
Collaborating with the project design team, the selection of frit pattern and ink is typically guided by the goal of meeting both light transmission and G-value/solar heat gain coefficient targets.
In conclusion, delving into the key components of an ETFE system is imperative to unlock the full potential of this revolutionary material. From the ETFE film itself to the intricacies of structural support, installation techniques, thermal control measures, and the vast realm of customisation options, each component plays a pivotal role in the success of an ETFE project. By embracing the unique properties of ETFE and seamlessly incorporating it into their designs, architects can craft sustainable, aesthetically pleasing and technologically advanced structures that not only redefine the possibilities of modern architecture but also stand as testaments to human ingenuity and innovation.
If you would like to learn more technical information about ETFE, visit our Knowledge page, or click below to download our Knowledge Series (ETFE) brochure